Slot Props Vue
You’re browsing the documentation for v2.x and earlier. For v3.x, click here.
This page assumes you’ve already read the Components Basics. Read that first if you are new to components.
Prop Casing (camelCase vs kebab-case)
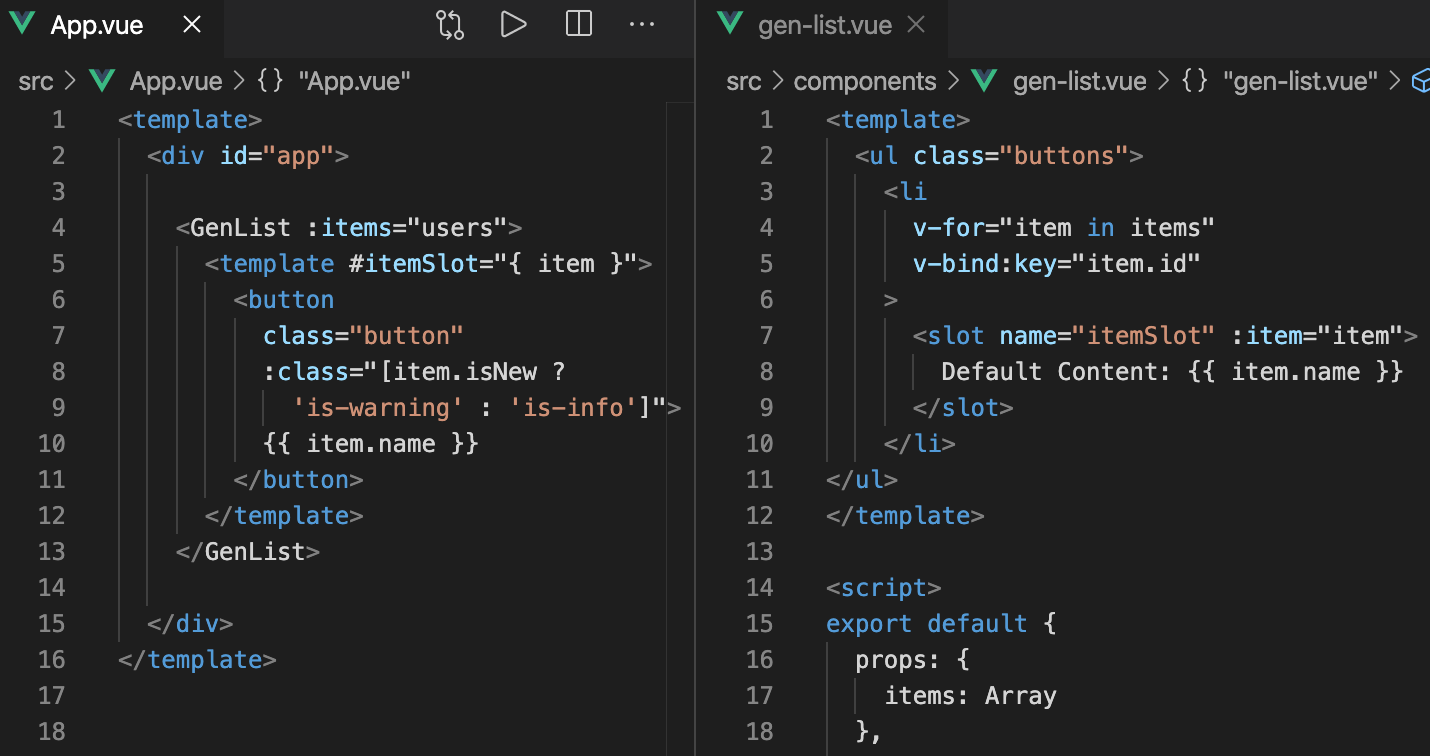
Note: Slots are supported only with vue-native-helper version 0.0.9 and above. Vue Native just like Vue implements a content distribution API that’s modeled after the current Web Components spec draft, using the slot element to serve as distribution outlets for content. When Vue 2.6.0 was released, Vue introduced a new unified syntax which is (the v-slot directive) for named and scoped slots. It replaced the slot and slot-scope attributes, which has been deprecated, though not removed, they are still document. Slot='someslot' slot-scope='props'. Practical Use Case of Vue Slots To pass down Html elements from one component to another. With props, Vue allows us to pass strings, objects, arrays, and functions from a parent component to its child component. Slot props allow us to turn slots into reusable templates that can render different content based on input props. This is most useful when you are designing a reusable component that encapsulates data logic while allowing the consuming parent component to customize part of its layout.
HTML attribute names are case-insensitive, so browsers will interpret any uppercase characters as lowercase. That means when you’re using in-DOM templates, camelCased prop names need to use their kebab-cased (hyphen-delimited) equivalents:
Again, if you’re using string templates, this limitation does not apply.
Prop Types
So far, we’ve only seen props listed as an array of strings:
Usually though, you’ll want every prop to be a specific type of value. In these cases, you can list props as an object, where the properties’ names and values contain the prop names and types, respectively:
This not only documents your component, but will also warn users in the browser’s JavaScript console if they pass the wrong type. You’ll learn much more about type checks and other prop validations further down this page.

Passing Static or Dynamic Props
So far, you’ve seen props passed a static value, like in:
You’ve also seen props assigned dynamically with v-bind, such as in:

In the two examples above, we happen to pass string values, but any type of value can actually be passed to a prop.
Passing a Number
Passing a Boolean
Passing an Array
Passing an Object
Passing the Properties of an Object
If you want to pass all the properties of an object as props, you can use v-bind without an argument (v-bind instead of v-bind:prop-name). For example, given a post object:
The following template:
Will be equivalent to:
One-Way Data Flow
All props form a one-way-down binding between the child property and the parent one: when the parent property updates, it will flow down to the child, but not the other way around. This prevents child components from accidentally mutating the parent’s state, which can make your app’s data flow harder to understand.
In addition, every time the parent component is updated, all props in the child component will be refreshed with the latest value. This means you should not attempt to mutate a prop inside a child component. If you do, Vue will warn you in the console.
There are usually two cases where it’s tempting to mutate a prop:
The prop is used to pass in an initial value; the child component wants to use it as a local data property afterwards. In this case, it’s best to define a local data property that uses the prop as its initial value:
The prop is passed in as a raw value that needs to be transformed. In this case, it’s best to define a computed property using the prop’s value:
Note that objects and arrays in JavaScript are passed by reference, so if the prop is an array or object, mutating the object or array itself inside the child component will affect parent state.
Prop Validation
Components can specify requirements for their props, such as the types you’ve already seen. If a requirement isn’t met, Vue will warn you in the browser’s JavaScript console. This is especially useful when developing a component that’s intended to be used by others.
To specify prop validations, you can provide an object with validation requirements to the value of props, instead of an array of strings. For example:
When prop validation fails, Vue will produce a console warning (if using the development build).
Note that props are validated before a component instance is created, so instance properties (e.g. data, computed, etc) will not be available inside default or validator functions.
Type Checks
The type can be one of the following native constructors:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- Date
- Function
- Symbol
In addition, type can also be a custom constructor function and the assertion will be made with an instanceof check. For example, given the following constructor function exists:
You could use:
to validate that the value of the author prop was created with new Person.
Non-Prop Attributes
A non-prop attribute is an attribute that is passed to a component, but does not have a corresponding prop defined.
While explicitly defined props are preferred for passing information to a child component, authors of component libraries can’t always foresee the contexts in which their components might be used. That’s why components can accept arbitrary attributes, which are added to the component’s root element.
For example, imagine we’re using a 3rd-party bootstrap-date-input component with a Bootstrap plugin that requires a data-date-picker attribute on the input. We can add this attribute to our component instance:
And the data-date-picker='activated' attribute will automatically be added to the root element of bootstrap-date-input.
Replacing/Merging with Existing Attributes
Imagine this is the template for bootstrap-date-input:
To specify a theme for our date picker plugin, we might need to add a specific class, like this:
In this case, two different values for class are defined:
form-control, which is set by the component in its templatedate-picker-theme-dark, which is passed to the component by its parent
For most attributes, the value provided to the component will replace the value set by the component. So for example, passing type='text' will replace type='date' and probably break it! Fortunately, the class and style attributes are a little smarter, so both values are merged, making the final value: form-control date-picker-theme-dark.
Disabling Attribute Inheritance
If you do not want the root element of a component to inherit attributes, you can set inheritAttrs: false in the component’s options. For example:
This can be especially useful in combination with the $attrs instance property, which contains the attribute names and values passed to a component, such as:
With inheritAttrs: false and $attrs, you can manually decide which element you want to forward attributes to, which is often desirable for base components:
Note that inheritAttrs: false option does not affect style and class bindings.
This pattern allows you to use base components more like raw HTML elements, without having to care about which element is actually at its root:
Swiper Vue.js components are compatible only with new Vue.js version 3
Installation
Swiper Vue.js plugin is available only via NPM as a part of the main Swiper library:
Usage
swiper/vue exports 2 components: Swiper and SwiperSlide:
By default Swiper Vue.js uses core version of Swiper (without any additional components). If you want to use Navigation, Pagination and other components, you have to install them first.
Here is the list of additional modules imports:
Virtual- Virtual Slides moduleKeyboard- Keyboard Control moduleMousewheel- Mousewheel Control moduleNavigation- Navigation modulePagination- Pagination moduleScrollbar- Scrollbar moduleParallax- Parallax moduleZoom- Zoom moduleLazy- Lazy moduleController- Controller moduleA11y- Accessibility moduleHistory- History Navigation moduleHashNavigation- Hash Navigation moduleAutoplay- Autoplay moduleEffectFade- Fade Effect moduleEffectCube- Cube Effect moduleEffectFlip- Flip Effect moduleEffectCoverflow- Coverflow Effect moduleThumbs- Thumbs module
Note, Swiper Vue.js component will create required elements for Navigation, Pagination and Scrollbar if you pass these params without specifying its elements (e.g. without navigation.nextEl, pagination.el, etc.)
Styles
Swiper package contains different sets of CSS, Less and SCSS styles:
CSS Styles
CSS styles for bundle version:
swiper-bundle.css- all Swiper styles including all components styles (like Navigation, Pagination, etc.)swiper-bundle.min.css- same as previous but minified
CSS styles for core version and components:
swiper.min.css- only core Swiper stylescomponents/a11y/a11y.min.css- styles required for A11y componentcomponents/controller/controller.min.css- styles required for A11y componentcomponents/effect-coverflow/effect-coverflow.min.css- styles required for Coveflow Effect componentcomponents/effect-cube/effect-cube.min.css- styles required for Cube Effect componentcomponents/effect-fade/effect-fade.min.css- styles required for Fade Effect componentcomponents/effect-flip/effect-flip.min.css- styles required for Flip Effect componentcomponents/lazy/lazy.min.css- styles required for Lazy componentcomponents/navigation/navigation.min.css- styles required for Navigation componentcomponents/pagination/pagination.min.css- styles required for Pagination componentcomponents/scrollbar/scrollbar.min.css- styles required for Scrollbar componentcomponents/thumbs/thumbs.min.css- styles required for Thumbs componentcomponents/zoom/zoom.min.css- styles required for Zoom component
Less Styles
Less styles are separate styles for core version and components:
swiper.less- only core Swiper stylescomponents/a11y/a11y.less- styles required for A11y componentcomponents/controller/controller.less- styles required for Controller componentcomponents/effect-coverflow/effect-coverflow.less- styles required for Coveflow Effect componentcomponents/effect-cube/effect-cube.less- styles required for Cube Effect componentcomponents/effect-fade/effect-fade.less- styles required for Fade Effect componentcomponents/effect-flip/effect-flip.less- styles required for Flip Effect componentcomponents/lazy/lazy.less- styles required for Lazy componentcomponents/navigation/navigation.less- styles required for Navigation componentcomponents/pagination/pagination.less- styles required for Pagination componentcomponents/scrollbar/scrollbar.less- styles required for Scrollbar componentcomponents/thumbs/thumbs.less- styles required for Thumbs componentcomponents/zoom/zoom.less- styles required for Zoom component
SCSS Styles
SCSS styles are also separate styles for core version and components:
swiper.scss- only core Swiper stylescomponents/a11y/a11y.scss- styles required for A11y componentcomponents/controller/controller.scss- styles required for Controller componentcomponents/effect-coverflow/effect-coverflow.scss- styles required for Coveflow Effect componentcomponents/effect-cube/effect-cube.scss- styles required for Cube Effect componentcomponents/effect-fade/effect-fade.scss- styles required for Fade Effect componentcomponents/effect-flip/effect-flip.scss- styles required for Flip Effect componentcomponents/lazy/lazy.scss- styles required for Lazy componentcomponents/navigation/navigation.scss- styles required for Navigation componentcomponents/pagination/pagination.scss- styles required for Pagination componentcomponents/scrollbar/scrollbar.scss- styles required for Scrollbar componentcomponents/thumbs/thumbs.scss- styles required for Thumbs componentcomponents/zoom/zoom.scss- styles required for Zoom component
Swiper props
Swiper Vue.js component receive all Swiper parameters as component props, plus some extra props:
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tag | string | 'div' | Main Swiper container HTML element tag |
| wrapperTag | string | 'div' | Swiper wrapper HTML element tag |
Swiper events
Swiper component supports all Swiper events, including additional swiper event that returns swiper instance as soon as posible. For example:
SwiperSlide props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tag | string | 'div' | Swiper Slide HTML element tag |
| zoom | boolean | false | Enables additional wrapper required for zoom mode |
| virtualIndex | number | Actual swiper slide index. Required to be set for virtual slides |
SwiperSlide slot props
SwiperSlide component has the following slot props:
isActive- true when current slide is activeisPrev- true when current slide is the previous from activeisNext- true when current slide is the next from activeisVisible- true when current slide is visible (watchSlidesVisibilitySwiper parameter must be enabled)isDuplicate- true when current slide is a duplicate slide (whenloopmode enabled)
For example:
Slots
Swiper Vue.js component uses 'slots' for content distribution. There are 4 slots available
container-start- element will be added to the beginning of swiper-containercontainer-end(default) - element will be added to the end of swiper-containerwrapper-start- element will be added to the beginning of swiper-wrapperwrapper-end- element will be added to the end of swiper-wrapper
For example:
Will be rendered as:
Virtual Slides
Virtual Slides rendering here is fully handled by Vue.js and not required anything except setting :virtual='true' property and setting virtualIndex on slides:
Controller
Controller requires to pass one Swiper instance to another:
For two-way control (when both Swipers control each other) it should be like this:
Vue Slot Props 違い
Thumbs
Same as with controller we need to store thumbs instance and pass it to main gallery:
Effects
The following effects are available:
- Fade
- Cube
- Overflow
- Flip
Slot-scope= Props Vuetify
To use effects you have to import and install them first (as all other modules) (Fade example):
Slot Props Vue Online
You can find running effect demos here.